Rosacea
Rosacea is a common and very chronic long term condition needing a long term consistent approach.
What are the symptoms of Rosacea
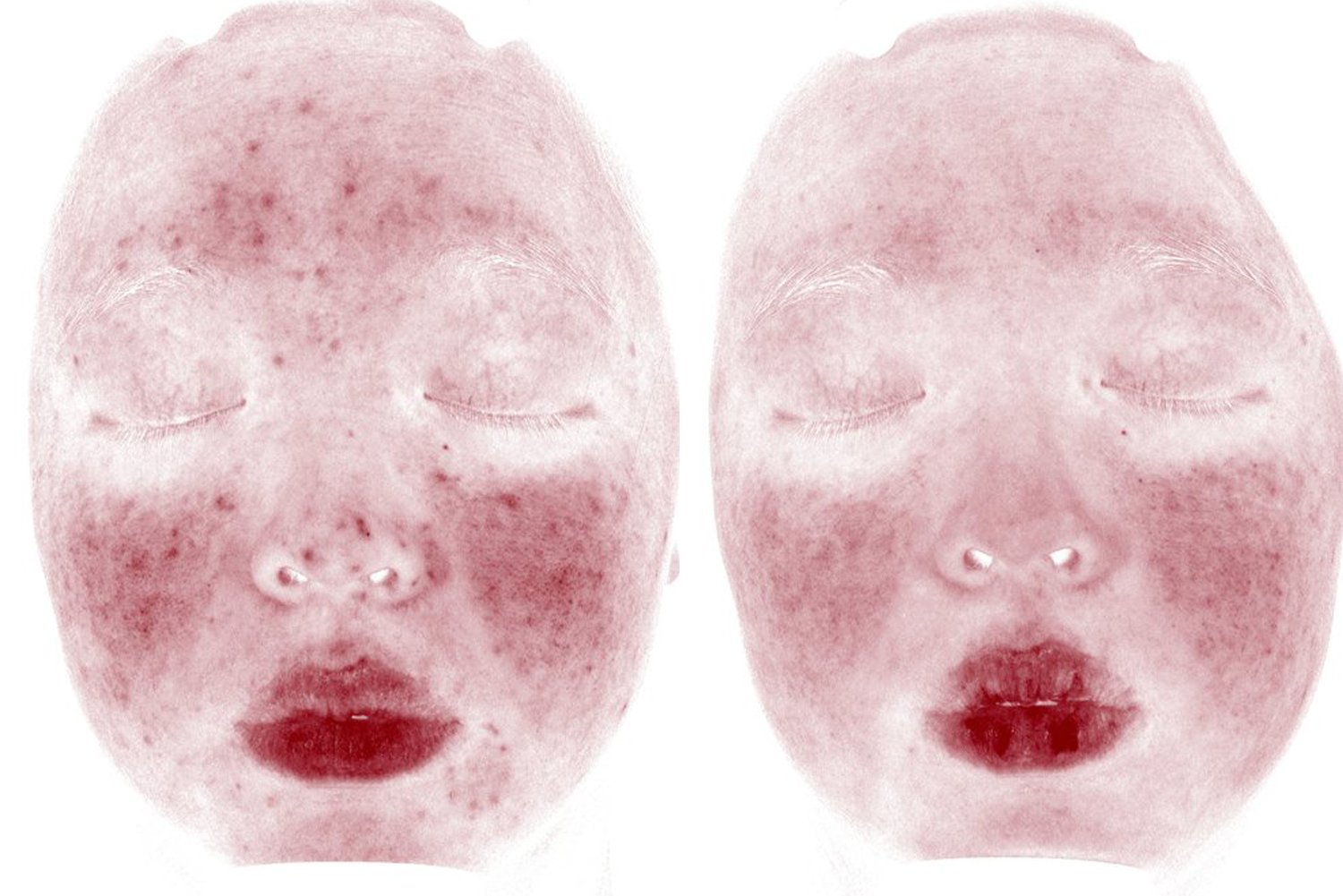
The symptoms of rosacea can include facial redness, flushing, and pimples, and can greatly impact a person's self-esteem and quality of life. It can often be confused with acne. What makes it different is that rosacea tends to occur in older patients and also involves flushing, broken blood vessels, and sensitive skin.
You may have rosacea if you have the following:
Flushing
Papules
Pustules
Telangiectasias (broken blood vessels)
Sensitive skin
Rosacea can sometimes affect the eyes in addition to the skin. This can lead to stinging or burning of the eyes or irritation with light. If eye symptoms occur, it is important to be seen by an ophthalmologist.
What is the cause of rosacea?
The cause of rosacea is not yet known but there are many theories that exist. We know that certain factors can aggravate or trigger rosacea and these include sunlight, menopause, topical anti-inflammatory creams, long hot showers, hot beverages, spicy foods, and also alcohol.
How is rosacea diagnosed?
Rosacea is usually diagnosed by the dermatologist clinically. This is because it presents with classic features with redness, broken blood vessels, and spots. These are red bumps but also pustules. Sometimes if there is confusion about the diagnosis or another diagnosis needs to be excluded such as lupus or sarcoidosis then a biopsy may be taken.
How we treat Rosacea: combining Medical & Laser Therapy
At NSDL, we create a personalised treatment plan based on your type of rosacea and skin needs. Combining medical and laser treatments is often the most effective strategy to address the different symptoms of rosacea. NSDL clinics approach is based on the latest scientific research, so as to provide patients with the most up-to-date and effective treatments available. After your skin is restored we will give you a strategy to keep your skin clear for years to come.
Medical Therapy for Rosacea
While medical treatments for rosacea do not reduce redness, they are essential for managing the pimples and bumps that can accompany the condition. We often prescribe topical treatments and, in moderate to severe cases, oral medications to control these symptoms.
TOPICAL CREAMS
These include metronidazole (Rozex), azelaic acid (Finacia) and ivermectin (Soolantra). These help with the papules and pustules. For inflammation, tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may also be used.
ORAL MEDICATIONS
These are also available for rosacea and include antibiotics. Usually, tetracyclines are used and this is to reduce inflammation and papule and pustule formation. If your rosacea is very severe or is resistant to this treatment, then you may require a course of isotretinoin. This is used at a very low dose over a longer period of time to enable side-effects to be dramatically reduced but also allowing for improvement of rosacea.
Laser Treatment for Rosacea
We use a variety of laser types to treat the redness and visible blood vessels associated with rosacea:
BBL 560 nm: Effective for reducing general redness and small blood vessels.
Candela VBeam Perfecta 595nm : Targets larger blood vessels, reducing the visible signs of redness.
755 nm laser: Treats deeper blood vessels and more stubborn redness.
CO2 laser: Occasionally used for specific cases where advanced resurfacing is needed.
These lasers target different blood vessel sizes, shapes, and depths, helping to clear redness and flushing for a more even skin tone.
What to expect during Laser treatment for Rosacea
Laser treatment for rosacea is typically performed in 2-3 sessions spaced 3-4 weeks apart:
No downtime: You can resume your normal activities immediately after treatment.
Minimal discomfort: Most patients experience a mild warming sensation during the procedure.
We recommend a follow-up appointment one month after your initial treatment, and maintenance treatments every 6 months to sustain the results long-term.
Sustaining Results
Rosacea is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. Once your skin has been restored, Dr. Wines will provide a personalized long-term strategy to keep your skin clear and prevent future flare-ups. This typically includes:
Regular maintenance laser treatments every 6 months
Continued medical therapy to control pimples and bumps
With this comprehensive approach, you can keep your rosacea under control for years to come.
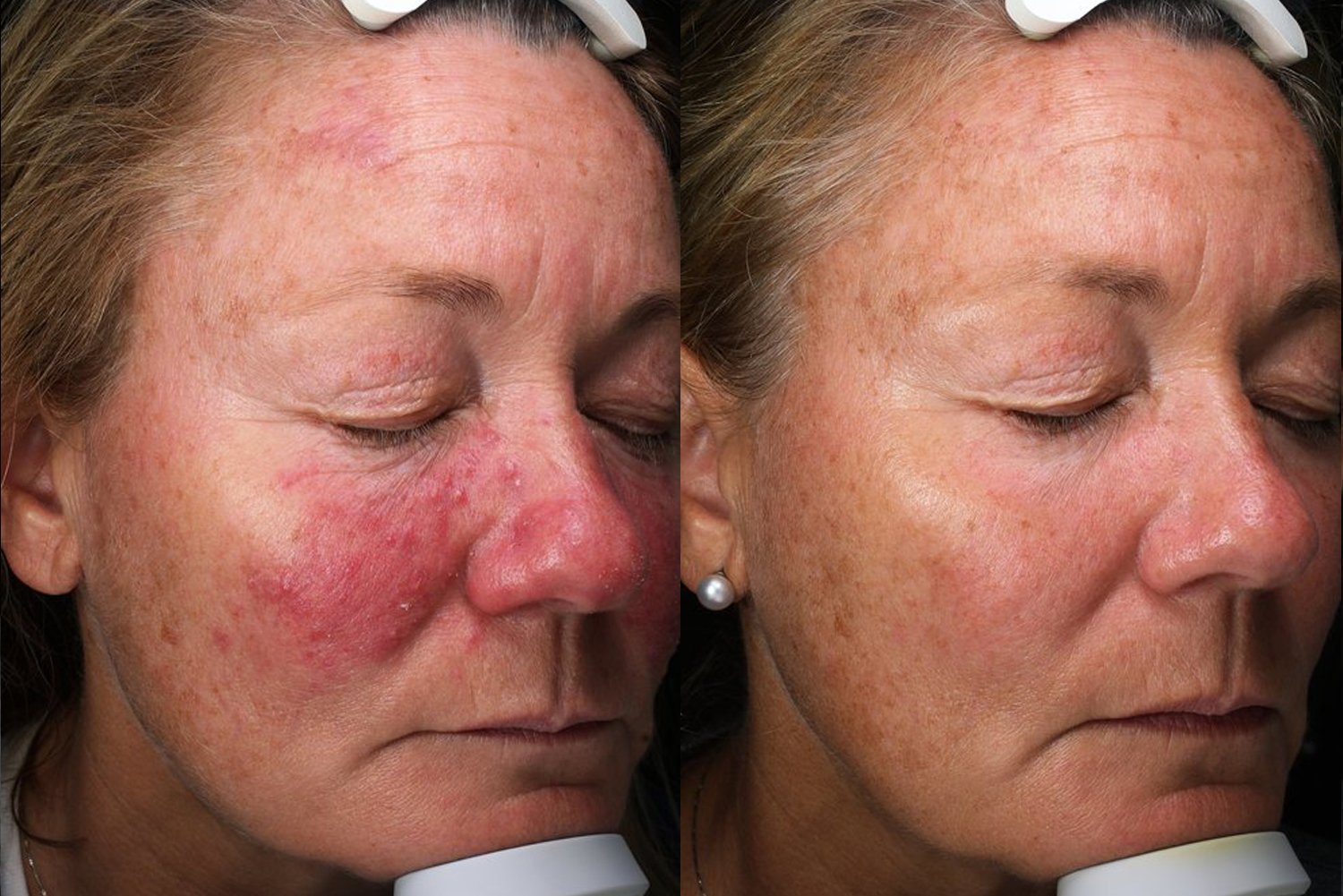
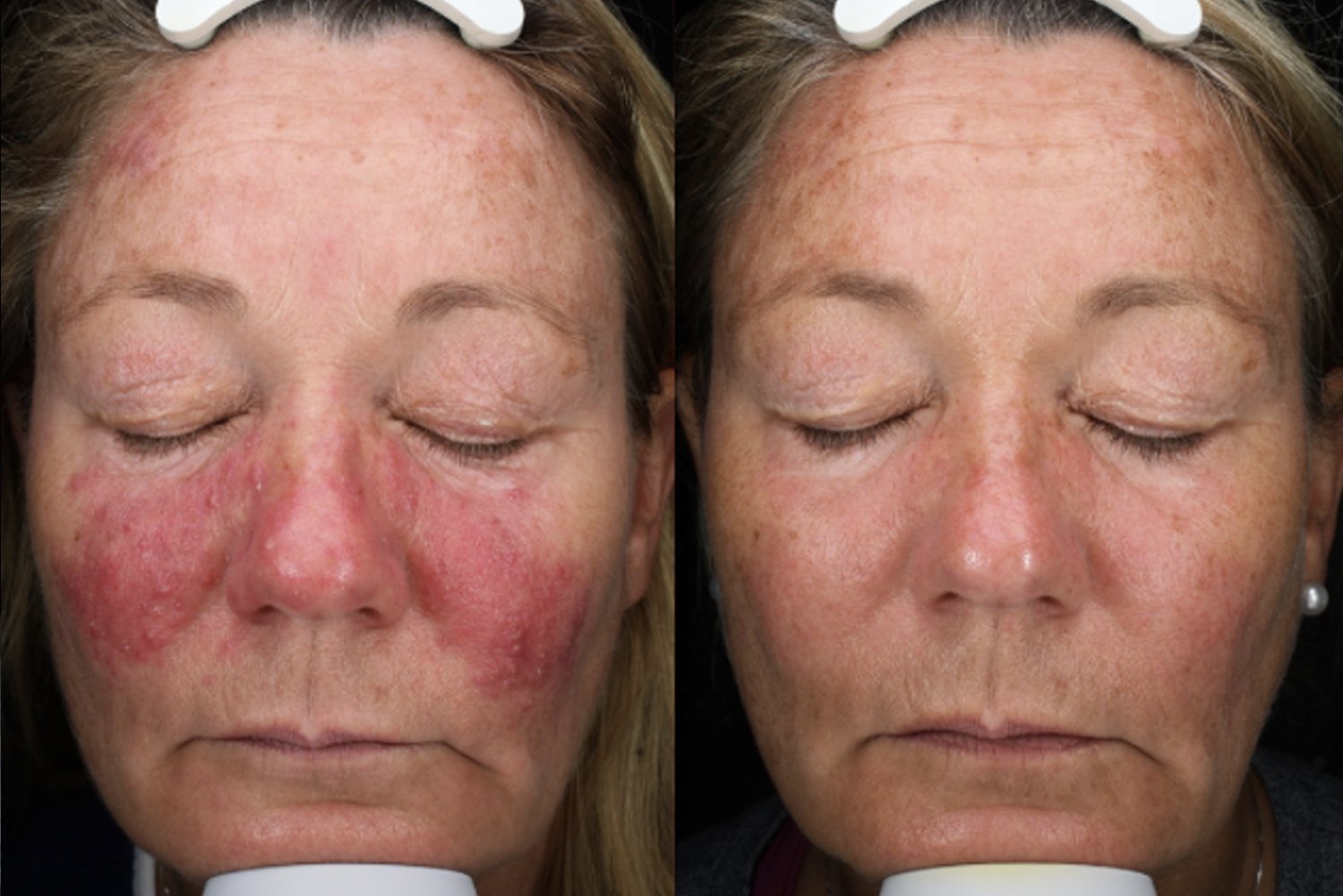
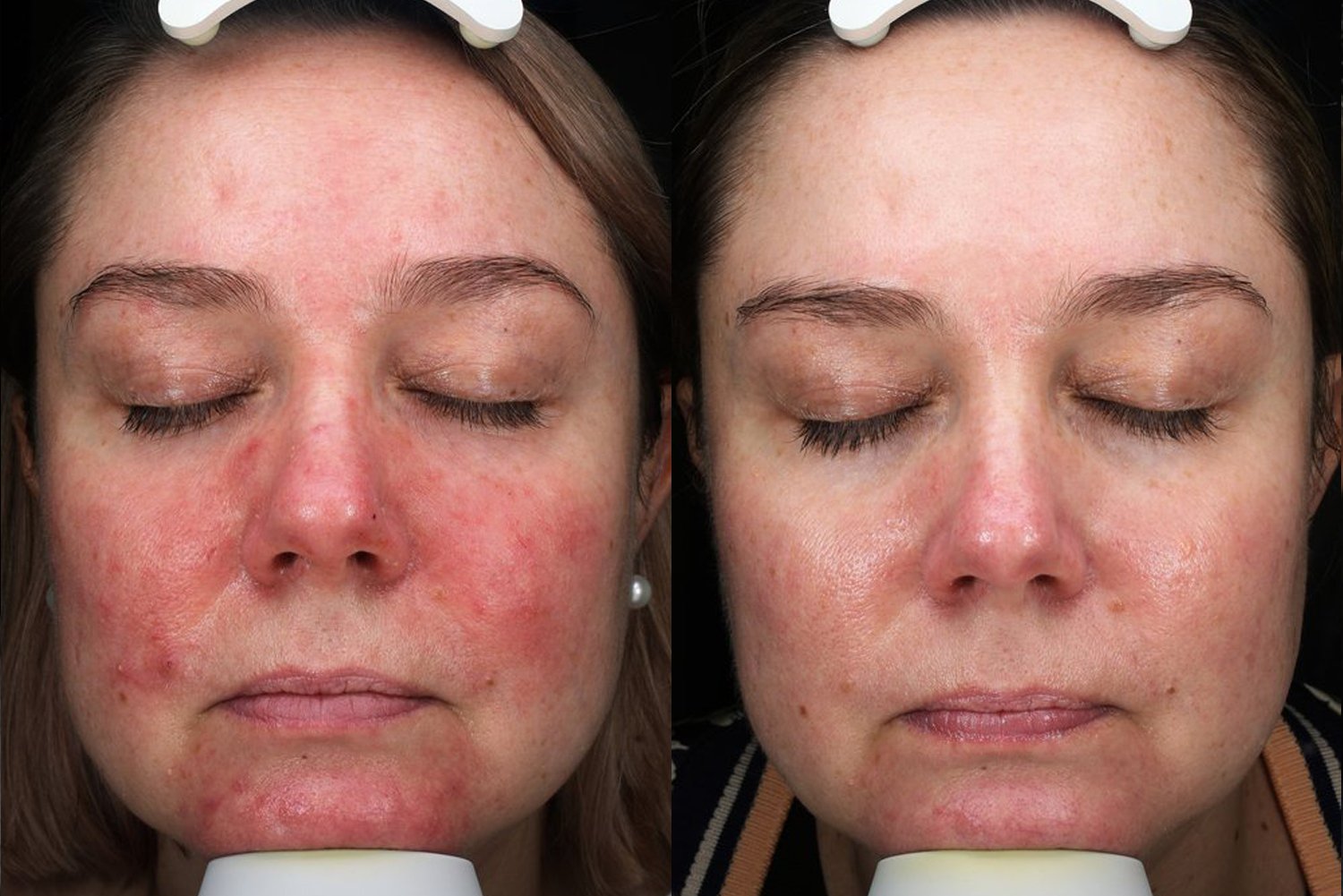
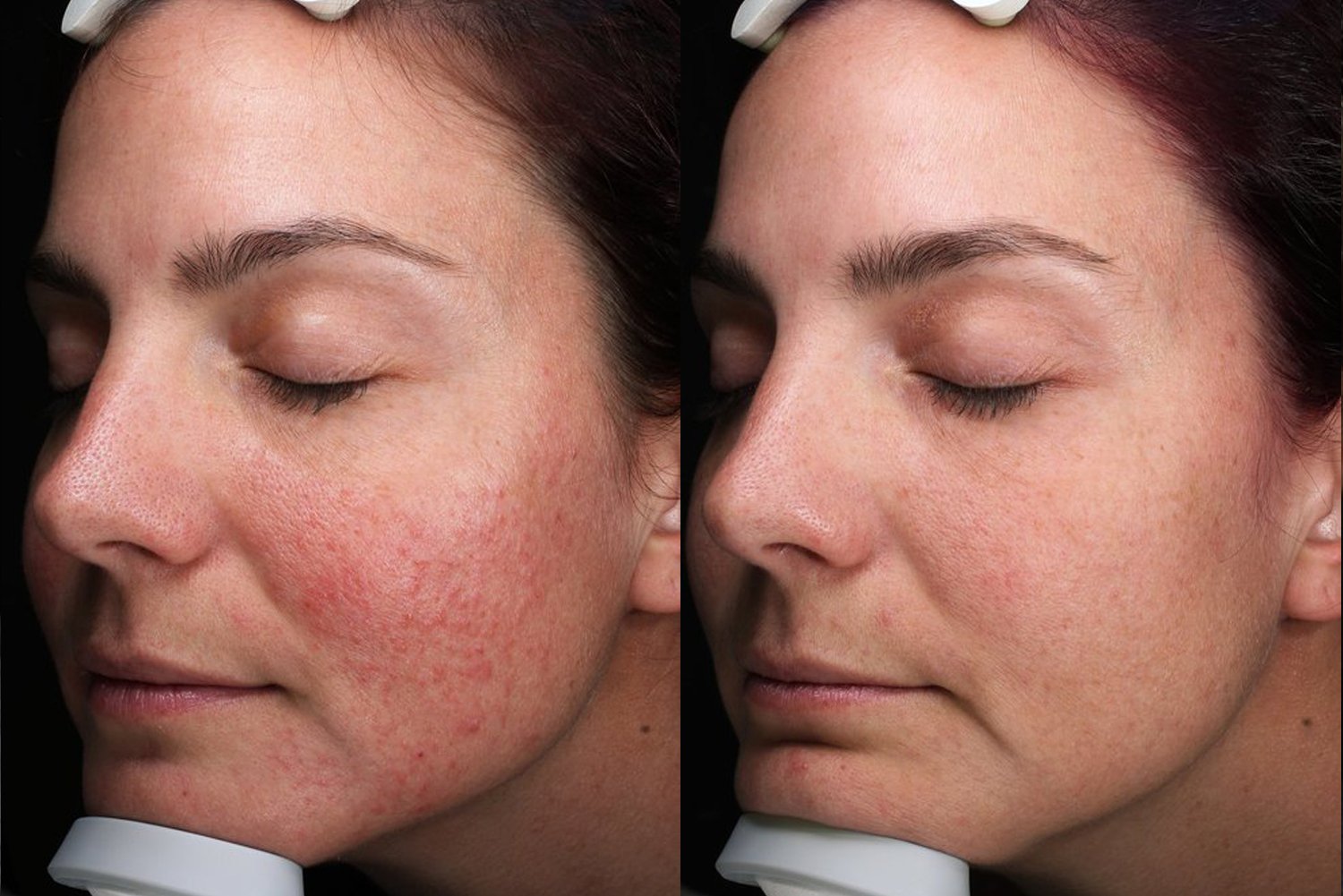
Book in for a Consultation with one of our Dermatologists below.
If you have already had a consultation with one of our Dermatologists, and are ready to book in your Laser Treatments, please phone: (02) 9958 1555.
All medical and cosmetic procedures involve some risks. The information provided here is for general educational purposes only. The results achieved for patients in before and after pictures are individual and may not be achievable for you specifically. For specific advice regarding your situation, please book an appointment at NSDL.










